Immunosuppressants: What They Are, How They Work, and What You Need to Know
When your immune system turns against your own body—attacking joints, skin, or organs—it’s not overreacting. It’s malfunctioning. That’s where immunosuppressants, medications that dampen the body’s immune response to prevent damage. Also known as anti-rejection drugs, they’re life-saving for people with autoimmune disorders or those who’ve had organ transplants. Without them, your body might reject a new kidney, attack your pancreas, or turn your skin into a battlefield. But they’re not magic pills. They come with real trade-offs.
These drugs don’t just calm down overactive immunity—they lower your body’s defenses overall. That means you’re more vulnerable to infections, from common colds to serious fungal or viral illnesses. People on long-term immunosuppressants often get regular blood tests to check white cell counts and liver function. They’re also warned to avoid raw meats, undercooked eggs, and sick people. Some of these drugs, like cyclosporine, a common transplant medication that blocks T-cell activation, can damage kidneys over time. Others, like azathioprine, an older drug used for lupus and Crohn’s disease, carry a small risk of raising cancer rates. And they don’t play nice with other meds. Antibiotics, antifungals, even some herbal supplements can spike or drop their levels dangerously.
It’s not just about taking a pill. Managing immunosuppressants means tracking symptoms, sticking to schedules, and knowing when to call your doctor. A fever, unusual fatigue, or sudden swelling could mean trouble. Many people on these drugs end up working closely with specialists—not just their primary care provider. The goal isn’t to shut down the immune system completely. It’s to find the sweet spot: enough suppression to stop damage, but not so much that you can’t fight off a simple infection.
The posts below cover real-world cases where these drugs come into play: how they interact with other treatments, what side effects patients actually face, and how people manage life while taking them. You’ll find details on drug combinations, monitoring tips, and red flags you shouldn’t ignore. Whether you’re on one of these meds, caring for someone who is, or just trying to understand why they’re so widely used, this collection gives you the facts without the fluff.
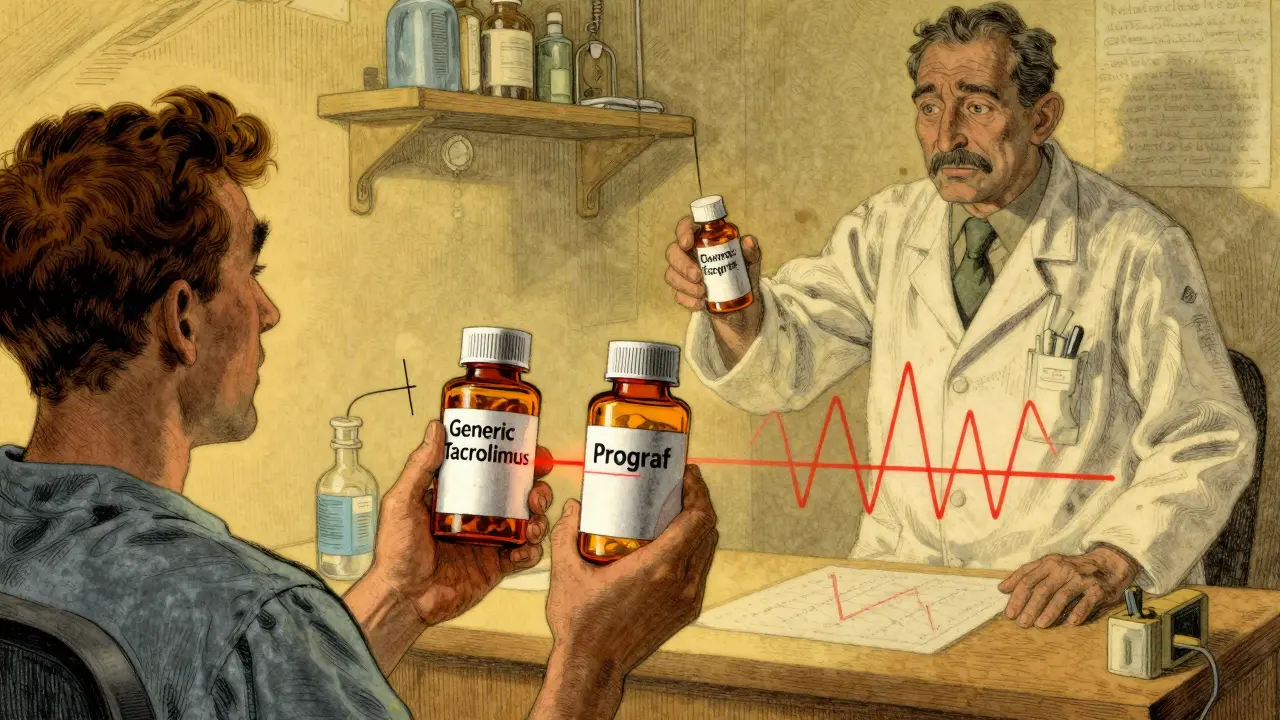
Cyclosporine and tacrolimus generics save money but carry serious risks for transplant patients due to their narrow therapeutic index. Learn why switching brands can trigger rejection, how to monitor levels safely, and what steps to take to protect your transplant.
Compare Prograf (Tacrolimus) with alternatives like Advagraf, cyclosporine, sirolimus, and belatacept. Learn which drugs work best for transplant patients based on side effects, cost, and long-term outcomes.