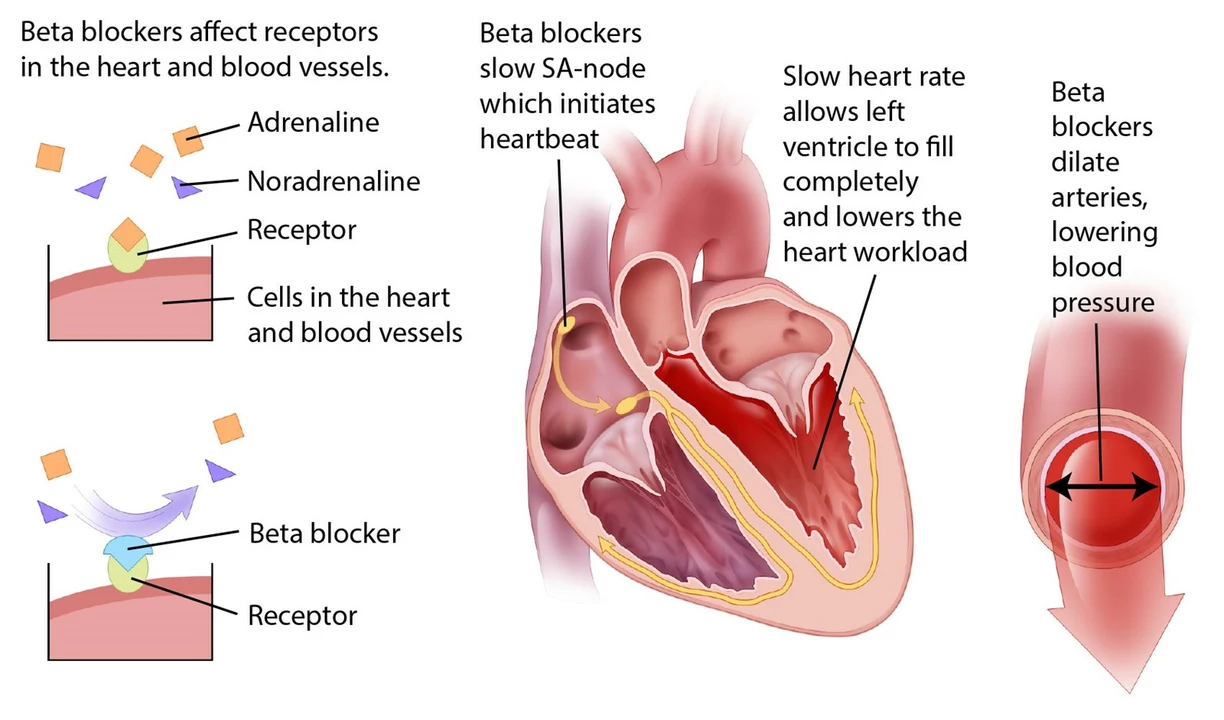
Beta-blockers: what they do and when you might need one
Want a quick, useful take on beta-blockers? These drugs lower heart rate and blood pressure by blocking adrenaline effects. Doctors prescribe them for heart issues, some anxiety problems, tremors, and migraines. They work differently from blood vessel relaxers or calcium channel blockers, so knowing when a beta-blocker fits matters.
How beta-blockers help
Beta-blockers blunt the body's “fight or flight” response. For people with high blood pressure, heart failure, angina, or after a heart attack, that calming effect reduces workload on the heart and can prevent further damage. Propranolol (Inderal) is a common one and also helps performance anxiety and tremors. Metoprolol and atenolol are used more for blood pressure and long-term heart care. They don't cure heart disease, but they lower risks and improve symptoms.
If you get stage fright or panic before a presentation, a short-acting beta-blocker can stop a racing heart and shaky hands without sedating you. Our article "Effective Performance Anxiety Remedies Beyond Inderal" covers options and real user tips if you need fast, practical help.
Practical tips & what to watch for
Side effects are usually predictable: tiredness, cold hands or feet, and slower heartbeat. People with asthma or COPD should be careful—some beta-blockers can tighten airways. If you have diabetes, they can mask low blood sugar signs like a fast heartbeat, so monitor glucose more closely. Stop or change dose only with your doctor—sudden withdrawal can trigger fast heartbeat or chest pain.
Interactions matter. Combining beta-blockers with other heart meds such as calcium channel blockers (like nifedipine) or certain antiarrhythmics can dangerously slow the heart or drop blood pressure. Read our piece "Understanding Nifedipine: How It Eases Angina" to see how different heart drugs compare and why your doctor balances them carefully. Also consider lifestyle triggers: alcohol and strong caffeine can affect rhythm and reduce drug benefits—see "Understanding Alcohol and Caffeine's Effect on Heart Rhythms."
Keep these simple habits: take doses at the same time daily, carry a list of your meds, and check pulse and blood pressure at home if your doctor asks. If you notice sudden shortness of breath, fainting, severe dizziness, or persistent fatigue, call your clinician. Labs and occasional ECGs help doctors adjust dose safely.
Want to read real-world takes? Our site includes hands-on posts like "Cardiologists Reveal the Real Pros and Cons of Daily Isosorbide Mononitrate" which helps compare nitrate therapy with beta-blocker strategies. For anxiety-focused readers, the performance anxiety article lists short-acting alternatives and behavioral tricks that pair well with or replace drugs when appropriate.
Final tip: beta-blockers are powerful and mostly safe when used right. Ask clear questions—what symptom are we treating, how will we measure success, and what side effects should I expect? That makes the difference between guesswork and a treatment that actually helps you live better.
Atenolol is a beta-blocker that I've recently researched in depth to better understand its uses and effects. It primarily helps in treating high blood pressure, angina, and irregular heartbeats by blocking the action of certain chemicals in the body. This medication has some common side effects like dizziness and fatigue, but it's essential to consult your doctor before stopping its use. In addition, it's crucial to follow the prescribed dosage and monitor any changes in our health. Overall, Atenolol can be an effective solution for managing specific heart-related conditions, but always remember to seek medical advice for proper guidance.